From this Report: | Click this Link: |
LUN Utilization Summary | Host |
Host Utilization Summary | Host |
Array Port Utilization | Host |
LUNs At Risk | Host |
Hosts At Risk | Name |

Server ID | The internal numeric ID of the server. |
Hostname | Host name links to Host Details. |
Location | Physical location of the host, if available. |
Display Name | The external host/server name. |
Make | Make of the server, if field is populated. |
IP Address | Host IP address. |
Model | Model of the server, if field is populated. |
Type | Type of server, such as TSM Media Server. |
Operating System | The host’s operating system. |
Last Poll Date | Last time the data was collected and stored in the portal database. |
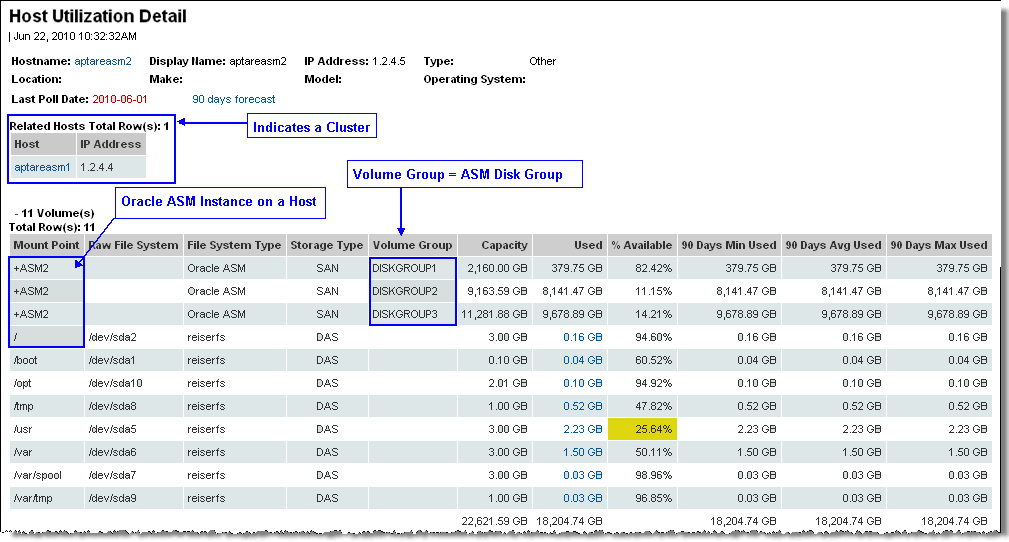
Mount Point | Mount point of the filesystem; for Oracle ASM, the mount point is the name of the ASM instance. |
Raw Filesystem | Filesystem name; for Oracle ASM, the raw filesystem is not applicable. |
Filesystem Type | When you know the filesystem type, you can determine the host’s storage requirements and limitations. Examples of filesystem values: • ASM - Oracle ASM • NTFS - Windows NT Filesystem • ext2, ext3 - Extended Filesystems 2 and 3 • ufs - Linux Filesystem • vxfs - Veritas Filesystem • FAT - File Allocation Table • hfs - Hierarchical Filesystem (Apple) • ctfs - Cooperative Temporary Filesystem • devfs - Device Filesystem • hsfs - High Sierra Filesystem • jfs - Journaled Filesystem • jfs2 - Journaled Filesystem 2 • nfs - Network Filesystem • objfs - Filesystem Object • sfs - Secure Filesystem • gpfs - General Parallel Filesystem (IBM) • proc - a virtual filesystem • procfs - Process Filesystem • tmpfs - a virtual memory filesystem • smbfs - Server Message Block Filesystem • Null - empty • NA - not applicable |
Storage Type | NAS - Network-attached storage; file servers and software dedicated to providing files over a network. SAN - Storage area network; Fibre Channel connected file servers. DAS - direct-attached storage; part of the host computer. MIXED - for Oracle ASM, if heterogenous storage is used. |
Volume Group | The volume group and logical volume names. For Oracle ASM, this is the ASM Disk Group name. |
Capacity | The host’s filesystem storage capacity. |
Used | The amount of the host’s storage that is currently in use. |
% Available | The percentage of the capacity that is unused. |
90 Days Min Used | Use these three columns in combination to substantiate the need for additional storage. Using 90 days worth of data, this provides a realistic snapshot of how the forecast was derived. |
90 Days Avg Used | The average 90-day usage. Using 90 days worth of data, this provides a realistic snapshot of how the forecast was derived. |
90 Days Max Used | The maximum usage for the past 90-day period. |
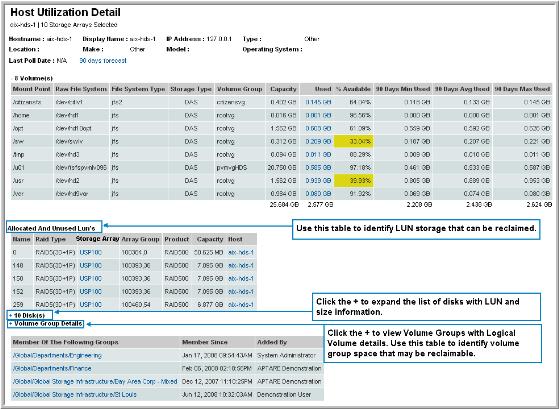
Mount Point | Mount point of the filesystem. |
Raw Filesystem | Filesystem name |
Filesystem Type | When you know the file system type, you can determine the host’s storage requirements and limitations. Examples of file system values: • NTFS - Windows NT Filesystem • ext2, ext3 - Extended Filesystems 2 and 3 • ufs - Linux Filesystem • vxfs - Veritas Filesystem • FAT - File Allocation Table • hfs - Hierarchical Filesystem (Apple) • ctfs - Cooperative Temporary Filesystem • devfs - Device Filesystem • hsfs - High Sierra Filesystem • jfs - Journaled Filesystem • jfs2 - Journaled Filesystem 2 • nfs - Network Filesystem • objfs - Filesystem Object • sfs - Secure Filesystem • gpfs - General Parallel Filesystem (IBM) • proc - a virtual filesystem • procfs - Process Filesystem • tmpfs - a virtual memory filesystem • smbfs - Server Message Block Filesystem • Null - empty • NA - not applicable |
Storage Type | NAS - Network-attached storage; file servers and software dedicated to providing files over a network. SAN - Storage area network; Fibre Channel connected file servers. DAS - direct-attached storage; part of the host computer. |
Capacity | The host’s filesystem storage capacity. |
Used | The amount of the host’s storage that is currently in use. |
% Available | The percentage of the capacity that is unused. |
90 Days Min Used | Use these three columns in combination to substantiate the need for additional storage. Using 90 days worth of data, this provides a realistic snapshot of how the forecast was derived. |
90 Days Avg Used | The average 90-day usage. Using 90 days worth of data, this provides a realistic snapshot of how the forecast was derived. |
90 Days Max Used | The maximum usage for the past 90-day period. |
Name | LUN name. |
RAID Type | The RAID type of the LUN. |
Storage Array | The storage array of the LUN links to the Array Capacity and Utilization. |
Array Group | The Array Group for the LUN. |
Product | Array product identifier. |
Capacity | Capacity of the LUN. |
Host | Links to the Host Utilization Detail. |
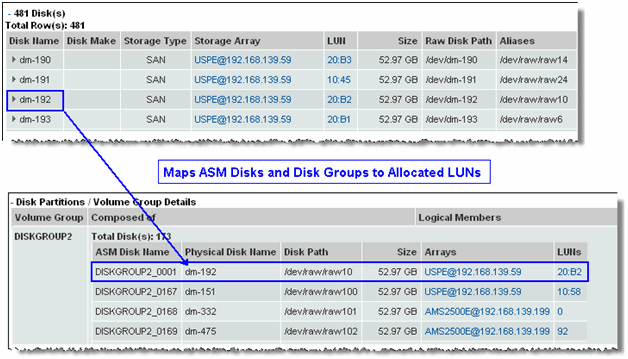
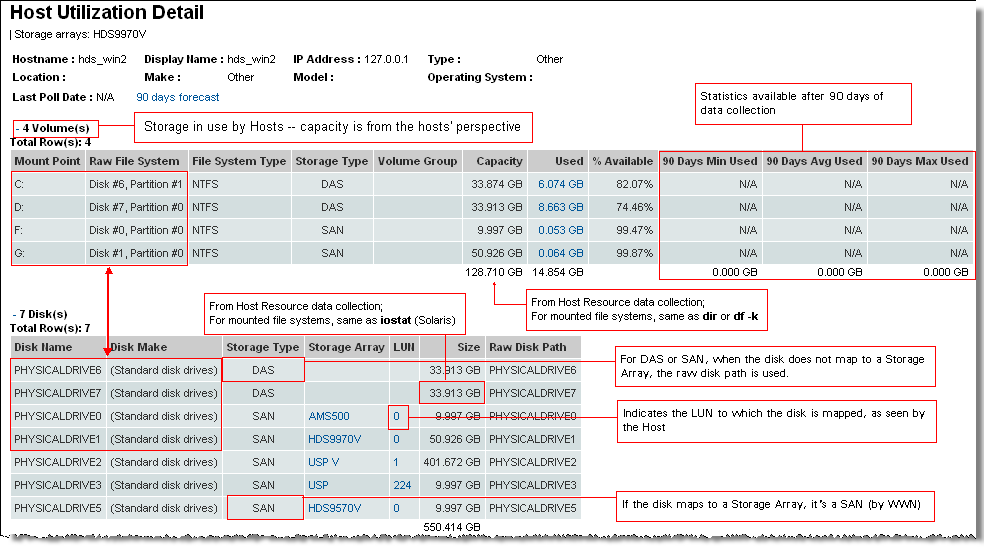
Disk Name | Disk name. |
Disk Make | The vendor information. |
Storage Type | DAS, SAN, NAS. |
Storage Array | The Array Group for the disk links to the Array Capacity and Utilization. |
LUN | The LUN links to the LUN Utilization Summary. |
Size | Disk size. |
Raw Disk Path | Disk path. |
Aliases | Aliases for the disk. |
Volume Group | The name of the volume group. |
Type | LUN or DSK. |
Name | LUN or Disk name. |
Array | Storage array; if this field is empty, it means it is a local disk. |
Physical Disk Name | Name of the disk. |
Size | Disk capacity. |
VVM Disk Capacity | Volume manager disk capacity. |
RAID Type | Disk or virtual disk RAID type associated with the storage pool. |
Disk Name | Name of the disk or virtual disk. |
Array | Array where the disk and LUN reside. |
Disk Capacity | Capacity that has been allocated. In the case of Oracle containers, this is the capacity allocated to the zones. |
Zone | Oracle VM (OS instance) |
Volume | If the volume value is blank, the Used value represents the data set used capacity. If there is a value listed for the volume, this means it is for a file system. |
Used | Represents the capacity “written to” the file system. |
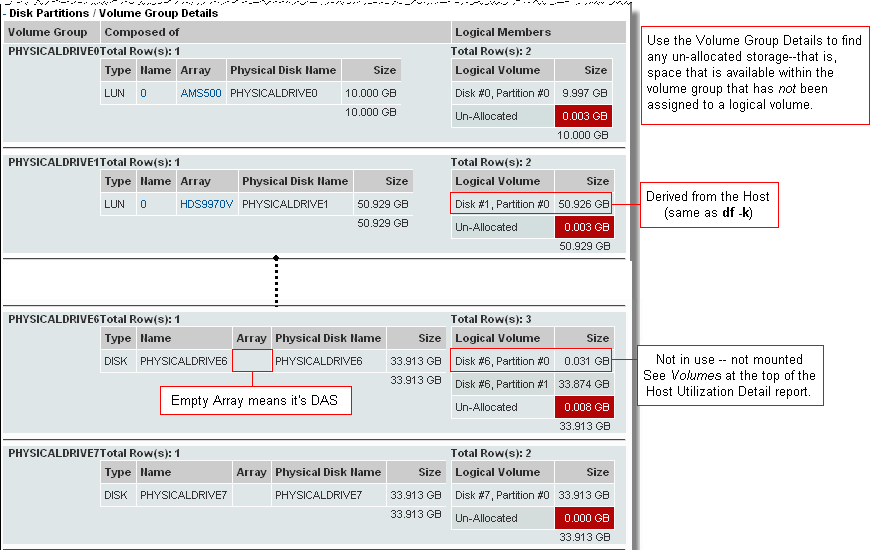
Logical Volume | The name of the logical volume. If listed as Un-allocated, it is not mounted. |
Size | Usable volume space. |
Physical Size | Physical size of logical member. |
Member Of The Following Groups | The full pathname of the host group links to additional host group details. |
Member Since | Indicates when this host became a member of the group. |
Added By | The user who added the host to the group. |
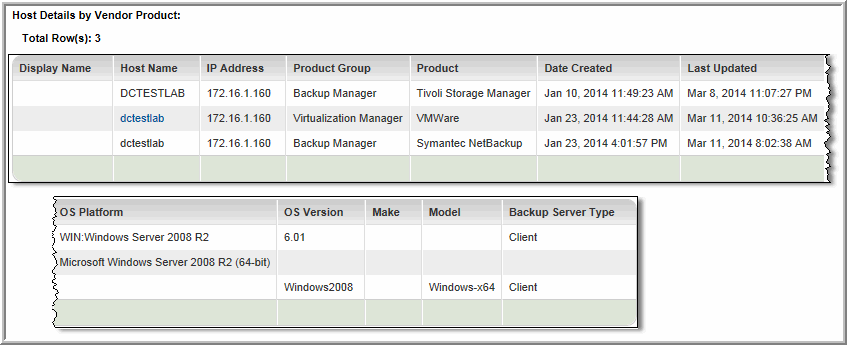
Display Name | Name that is displayed in reports. |
Host Name | Name of the host as it was collected by the vendor product. |
IP Address | IP address of the host. |
Product Group | The APTARE StorageConsole group, such as Capacity Manager, for which the host data was collected. |
Product | A specific vendor product (subsystem) from which host data was collected; for example, VMware. |
Date Created | The date and time the host was created in the StorageConsole database. |
Last Updated | The date and time the host data was updated in the StorageConsole database. |
OS Platform | Operating system of the host, as collected from this vendor product; for example, Windows Server 2008 R2. |
OS Version | The host’s specific operating system version, as collected from this vendor product; for example, 6.01. |
Make | The host’s make, as collected from this vendor product; for example,Windows-x64. |
Model | The host’s model, as collected from this vendor product; for example, PowerEdge 2950. |
Backup Server Type | The host’s role in a backup relationship, client or server. |