
Function | Description | Examples |
AVG | Calculates the average of the values from the selected column. | Display the average hours worked for a department. |
COLLECT | Takes a database column and creates a nested table from the selected rows; associates a list of data with a specific value, enabling aggregation of data into a collection. | Create a list of employees within a department. |
COUNT | Lists the number of rows returned from the database for the selected column. | Determine the number of employee records returned from a database query. |
MAX | Returns the maximum value of the selected column’s values. | Display the maximum hours worked. |
MIN | Returns the minimum value of the selected column’s values. | Display the minimum hours worked. |
STDDEV | Returns the standard deviation of the selected column’s values. | Apply standard deviation to values, for example, for forecasting. |
SUM | Calculates the sum of the values from the selected column. | Display the total hours worked for a department. |
Function | Description | Examples |
GREATEST | From a list of expressions, Oracle determines which has the highest numeric precedence. For Oracle’s data type comparison rules, see http://docs.oracle.com/cd/B19306_01/server.102/b14200/sql_elements002.htm#i55214 | The following query results in BELIZE: SELECT GREATEST('BELIZE','BELGIUM','BELARUS') "GREATEST" FROM DUAL |
LEAST | From a list of expressions, Oracle determines which has the lowest numeric precedence. For Oracle’s data type comparison rules, see http://docs.oracle.com/cd/B19306_01/server.102/b14200/sql_elements002.htm#i55214 | The following query results in BELARUS: SELECT LEAST('BELIZE','BELGIUM','BELARUS') "LEAST" FROM DUAL |
Function | Description | Examples |
CEIL | Returns the smallest integer value that is greater than or equal to the value (n). | 13551.8 becomes 13552 |
FLOOR | Returns the largest integer value that is less than or equal to the value (n). | 13551.8 becomes 13551 |
ROUND | Rounds a number to the specified number of decimal places: Negative arguments indicate rounding to the left of the decimal point. Positive arguments round to the right of the decimal point. | 25.193 with an argument of 1 will round to 25.2 |
SIGN | Returns a number that represents the sign of a value (n). | -1 if n < 0; 0 if n = 0; 1 if n >0 |
TRUNC | Truncates a value to the specified number of decimal places. | 25.193 with an argument of 1 will truncate to 25.1 |
Function | Description | Examples |
aptStringConcat | Creates a comma-separated list of strings. The Oracle function, aptStringConcat with DISTINCT or UNIQUE, cannot be used to concatenate values in a method, even though the method will validate and save. When that method is used in a report template, it will fail. Use collectString in a method to get this functionality. | aptStringConcat (array_name) can be used to create a comma-separated list of arrays within an array family. |
collectString | Use this function in the Method Designer to concatenate distinct values. See the APTARE Database Programmer’s Reference Guide for additional examples. | SELECT rtd.collectString(SET(CAST(COLLECT(cast(client_id as varchar2(10))) AS stringListType)),', ') name from apt_v_job; |
CONCAT | Concatenates multiple character strings. | 'Storage' + 'HQ' = 'StorageHQ' |
INITCAP | Displays a string with the first letter of each word in uppercase. | 'daily backup schedule' becomes 'Daily Backup Schedule' |
LOWER | Displays a string with all letters of each word in lowercase. | 'DAILY BACKUP SCHEDULE' becomes 'daily backup schedule' |
LPAD | Pads the left of a string with the specified characters, up to the total string length. | Preface an alert message with a string of asterisks; for example, ****Warning |
LTRIM | Trims the specified character set from the left of a string. This is useful for removing redundant words, characters, or labels. When no string is supplied, it defaults to a single blank. | 'RAID5' and 'RAID6' would be trimmed to simply '5' and '6' |
REPLACE | Substitutes one character string for another character string; in addition, you can remove character strings. | Substituting 'HDS' for 'Hitachi' changes 'Hitachi array' to 'HDS array' |
RPAD | Pads the right of a string with the specified characters, up to the total string length. | Postfix text with a string of asterisks; for example, Error*** |
RTRIM | Trims the specified character set from the right of a string. This is useful for removing redundant words, characters, or labels. When no string is supplied, it defaults to a single blank. | 'RAID 5' and 'RAID 6' could be trimmed to simply 'RAID' |
SUBSTR | Extracts a portion of a character string. | Use this function to list the first three characters of policy names. |
TO_DATE | Converts a character string to a date. | to_date('10/09/13', 'DD/mm/YY') to_date('10-sep-13', 'DD-MON-YYYY') |
TRANSLATE | Makes several single-character substitutions; one-to-one substitution in one operation. | Use this function to replace all spaces with an underscore character. 'System Reference Guide' would become 'System_Reference_Guide' |
TRIM | Removes leading or trailing characters (or both) from a character string | Use this function to remove leading zeroes from object identifiers (00049 --> 49) |
UPPER | Changes all characters in a string to uppercase | 'hds' becomes 'HDS'; 'Aptare' becomes 'APTARE' |
Function | Description | Examples |
ADD_MONTHS | Takes the date and adds n months. The result has the same day as input date. If the input date is the last day of the month or has fewer days than the resulting month, then the returning date will be the last day of the month. | June 22nd + 3 = September 22nd |
ROUND | Rounds the date to the unit format that you specify: Minute, Hour, Day, Month, Quarter, Year. | If you specify Month, the function rounds up on the 16th day of the month |
SYSDATE | Returns the current date and time for the system on which the database resides. | 06-13-2012 09:34:41 (displayed in the format: MM-DD-YYYY HH:MM:SS) |
TO_CHAR | Converts a date or interval value to a character data type in the specified format: Date, Timestamp. | finish_Date, 'DD-MON-YYYY HH24:' startDate, 'YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS' |
TRUNC | Truncates the time portion of a day to the specified format unit: Minute, Hour, Day, Month, Quarter, Year. In Oracle, date values contain a year, month, and day and also the hour, minute, and second. | 10-July-2012 09:34:41 becomes 10-July-2012 |
Function | Description | Examples |
INSTR | Searches a string for a sub-string and returns an integer that is the position in the string of the first character of the sub-string. The INTSR and LENGTH functions are mutually exclusive. | Search for 'error' in the string: 'A big system error caused the problem.' This results in 14. |
LENGTH | Returns the number of characters of a character string. The INTSR and LENGTH functions are mutually exclusive. | Length of 'array type' would be 10 |
Function | Description | Examples |
NVL | Checks for a null and substitutes another value. | Use this function to display N/A instead of a blank value |
Function | Description | Examples |
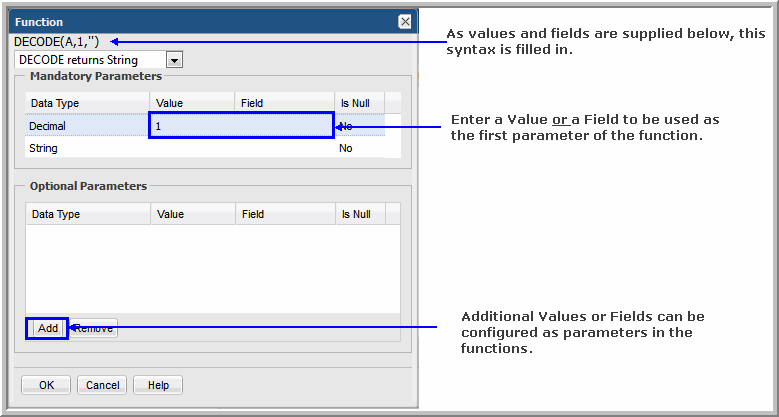
DECODE | Checks for a value and if there is a match, replaces it with another constant or database field value. | Use this function to display Success if the status is 0, Warning if the status is 1, and Failed if the status is 0. DECODE(summary_status, 0, 'Success', 1, 'Warning', 2, 'Failed') |
Function | Description | Examples |
UNIQUE | Enables aggregation on a unique field. This function can be applied to only one field in a report template. | COUNT(UNIQUE(client_id)), MAX(UNIQUE(server_id)), job_type FROM apt_job GROUP BY job_type |
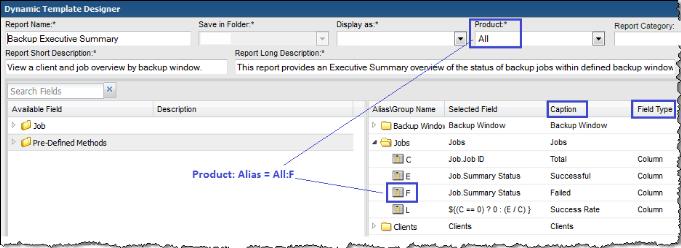
Report Template | Report Type | Product: Alias | Caption | Field Type | Functions |
Backup Manager Reports | |||||
Backup Executive Summary | Table | All: F | Failed | Column | DECODE, SUM |
All: G | Failed Count | Hidden | DECODE, UNIQUE, COUNT | ||
All: U, All: V | Start Date | Hidden | MAX | ||
All: C | Total | COUNT | |||
All: D | Total | UNIQUE, COUNT | |||
Job Status Summary | Bar | All: T | Failure | Bar | DECODE, SUM |
Job Summary | Table | Veritas NetBackup: P1 | Client | Column | NVL |
Veritas NetBackup: O1 | Host Id | Hidden | NVL | ||
CommVault Simpana: X1 | Reason | Column | DECODE | ||
CommVault Simpana: R | Reason | Hidden | NVL | ||
Tivoli Storage Manager: C | Server | Column | UPPER | ||
HP Data Protector: V | Status | Column | NVL, DECODE | ||
Job Volume Summary | Bar | All: D | # of Files Backed Up or Restored | Line | SUM |
All: B | # of Jobs | Hidden | COUNT | ||
All: C | Backup/Restore Volume | Bar | SUM | ||
Job Duration | Bar | All: F | Job Duration | Bar | SUM |
Error Log Summary by Server | Table | All: E | Error Occurrences | Column | COUNT |
All: F | Last Error Date | Column | MAX | ||
Error Log Summary by Client | Table | All: F | Error Occurrences | Column | COUNT |
All: G | Last Error Date | Column | MAX | ||
Error Log Summary by Policy | Table | All: E | Error Occurrences | Column | COUNT |
All: F | Last Error Date | Column | MAX | ||
Consecutive Errors By Client | Table | All: N | # Consecutive Errors | Column | COUNT |
All: I | First Error Date | Column | MIN | ||
Largest Backup Volume | Pie | All: C | Job Size | Sector | SUM |
Data Domain Reports | |||||
Data Domain Snapshot History | Table | EMC Data Domain: K | Days Left To Expire | hidden | TRUNC |
EMC Data Domain: I | Expires After (Days) | Column | SIGN, DECODE, TO_CHAR, NVL | ||
Capacity Manager Reports | |||||
Array Executive Summary | Table | All: A1 | Thin | Column | SUM, NVL |
LUN Utilization Summary | Table | All: F Hitachi Data Systems: C Symmetrix: D NetApp: E IBM: E IBM XIV: E IBM SVC: E HP EVA: C | Device Nbr | hidden | TO_CHAR, LPAD |
NetApp Cluster-Mode Volume Summary | Table | NetApp Cluster-Mode: N | Type | Column | UPPER |
EMC Isilon Nodes | Table | EMC Isilon: Y | # Int Up Interfaces | Column | DECODE, TO_NUMBER, SUM |
EMC Isilon: T | External IP Address | Column | DECODE, aptStringConcat | ||
EMC Isilon File System Performance by Protocol | Line | EMC Isilon: H | Max Bytes Out | Line | MAX |
EMC Isilon: A | # Active Clients | Line | AVG | ||