Report Scope
Before generating a report, you select enterprise objects such as the storage arrays, hosts or host groups, fabrics, zones, or switches to include in the report scope.
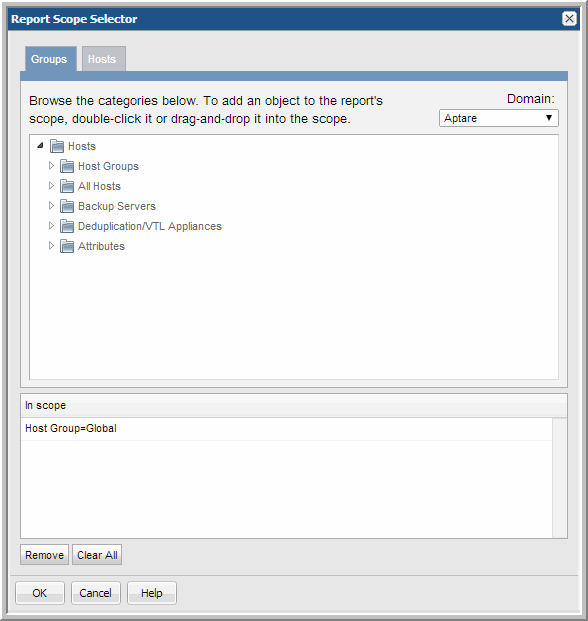
• Host Groups. Host groups primarily serve as a means of enforcing security controls, limiting a user’s access to only the hosts in a user’s APTARE IT Analytics domain. In the context of report scope, host groups are relevant for backup, host capacity, file analytics, and virtualization management reporting. In addition, several related sub-categories can be selected to narrow report scope, depending on the type of data the report supports: Devices, Shares, Volumes, and Deduplication/VTL Appliances. When selecting host groups in the Scope Selector, the selections are displayed in the bottom display panel.
Attributes provide an alternate grouping mechanism for a report scope. See also,
Host Groups vs Attributes.
• Hosts. Select specific hosts for a static report. A static report does not take into account changes in your network topology, so if you add clients to a network, you either have to explicitly include them in your report scope or add them to a host group. To ensure that host are always included in reports, assign them to a host group and select host groups for your report scope. For backup reports, a variety of components can be selected to be available in the Report Template’s scope selector; for example, Consecutive Errors, Ignore Retries, and Backup Window. For certain host reports, additional options may be available to filter the scope of the report, such as OS Platform (such as Windows or Linux), Product Collected (find hosts that have been collected from a particular subsystem, such as Veritas NetBackup), and Product Not Collected (find hosts that may be unprotected because they have not been collected from a particular subsystem, such as EMC Avamar). Reports list the full path of the host group in report headers. When selecting host groups in the Scope Selector, the selections are displayed in the bottom display panel.
• Host Type. Indicates how a host has been commissioned in an enterprise, such as VM Guest, VM Server, VIO Guest, VIO Server, Oracle Container, Oracle Zone, Hyper-V Server, Hyper-V Guest or Others.
• Datastores and Hypervisors. For Virtualization Manager, datastores and hypervisors can be selected for a report scope.
• Clusters. For Virtualization Manager, clusters can be selected for a report scope. Clusters refer to the way ESX servers are grouped.
• Arrays. For capacity reports, select any of the following: storage array, array family, array vendor, or array product.
• SAN Fabrics (including Zones and Switches). Select specific SAN Fabric objects to narrow the scope of a report.
• Attributes. Attributes associated with objects such as hosts, storage arrays, libraries, drives, switches, host Oracle database, and host MS Exchange, enable logical groupings for reports; for example,
OS version could be an attribute that you want to associate with hosts. Attributes enable you to define a data set based on a specific characteristic. For more information, see
About Attributes and
Host Groups vs Attributes.
Report scope objects are grouped into a hierarchical format, enabling disparate groupings. For example, hosts can be grouped by vendor, geography, department, and so on. This object grouping also provides additional data partitioning (security) by restricting a user’s view to hosts under the home host group. In addition, various built-in processes organize hosts based on information available from backup products; for example, group by master server or group backup servers by policy.
When you generate a report, a database query is initiated, based on the report scope that you specify. Since the nature of your IT environment is dynamic—for example, it’s not uncommon to add host groups and hosts to your network—reports reflect the updates.
Use the following guidelines to ensure that your reports include the data you expect to see:
• If you add new host groups after you generate a report, the next time you generate this same report, it will include different results. When you scope by host group or attributes, a dynamic report is produced.
• If you add hosts to your network, but do not assign them to a group, then generate a report without including the new hosts in your scope, you can be certain that the data for that host will not be in the report. This type of report scope produces a static report. However, if you add the host to a host group and this group is part of the report scope, the report automatically includes report data for that host.
For possible scope selections specific to an enterprise object, see:
Selecting Report Scope
You can create static reports or dynamic reports. To create static reports, define your report scope based on a list of individual enterprise objects, such as hosts or arrays. To produce dynamic reports, define your report scope based on domain, host groups, and attributes.
To learn about how report scope selects objects. Go to
Report Scope. For advanced report filtering, see
Advanced Filtering for Tabular Reports.
Report scope operates with the following logic:
• Report scope is restricted to objects of the same type, such as arrays and array vendors, but not host groups.
• Detail reports have limited report scope capabilities. For reports that are the result of drilling into details from a parent report, those detail reports can have their own unit of measure, separate from the parent report settings. Once you’ve drilled into a child report, you can edit the report scope and use the Advanced option to change the measurement unit to see more accurate or easily understandable information. For example, an Array Capacity & Utilization report shows aggregated data in TiB.When you drill down to a detail report, it may be more useful to switch to MiB.
Time Period Considerations
• Certain reports, such as the Array Performance by RAID Group, query database tables for daily log data. When choosing a scope of less than 24 hours and no data is returned, make sure that the report scope time period includes the 12 a.m. midnight boundary.
• For Backup Manager reports: The time period used to retrieve a report’s data takes into account the time zone of the collected systems, if relevant. For example, if 15 minutes is selected for a report that has a backup server in Hong Kong, but the report is being generated in San Francisco, the time period reflects the 15-minute interval and the end time will be the end of the Hong Kong server’s day. If there is no data collected from a different time zone, the Portal’s local time is used.
• For non-backup reports and SQL Template Designer reports: The precise start and end times for the time period will be displayed, without consideration of time zones.
• For data collection reports: you can select the Run Time either for scheduled or on-demand collection to narrow the scope. Select from Last Run up to the Last 7 Days.
To select report scope
1. Search for a report to generate. For example: Job Summary
The Job Summary Scope Selector allows you to specify parameters, report criteria and generate a report as shown in the following example:
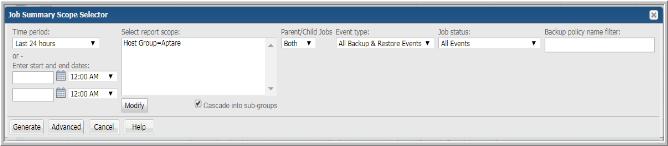
2. Click Modify. The Report Scope Selector window launches.
The tabs in the Report Scope Selector vary based on the report type. This window enables you to:
• Expand the list of available objects.
• Double-click to add an object to the scope - Report scope is restricted to objects of the same type, such as arrays and array vendors, but not host groups.
• Double-click to remove an object from the scope - This removes an object that has been place in the report scope.
• Drag and drop objects into the scope - Click the object and move it until you see a red dotted rectangle. Drop it into the In scope pane.
3. For reports with a host in the report scope, you can:
• Create a dynamic report. In the Groups tab, select the group of hosts that you want to include in your report:
• If you want to begin by including all hosts, select the entire domain—the top-level host group.
• If you want to begin by including specific hosts within a host group, select the check box for that host group.
• Create a static report. Select a list of individual hosts that you want to include in your report:
• In the Groups tab, drill down to each client’s host group and select the client’s check box; or
• Go to the Groups tab and create a list of hosts based on attributes.
4. Select attributes from the
Attributes folder to include objects that have the attribute value assigned to them. Attributes provide a way of defining a set of objects that share a certain characteristic. When you include an attribute in a report’s scope, you include all objects that have this attribute value. See also,
Host Groups vs Attributes.
5. Click OK.
Configuring Report Scope with Attributes
Attributes enable you to define a set of data to populate reports. In addition, attributes provide flexibility for categorizing data. For example, you may want to organize hosts by location and business unit. For more information on how to create and manage attributes, see
Managing Attributes and Objects,
Setting Attributes on Hosts, and
Host Groups vs Attributes.
To configure a report’s scope using attributes
1. Search for a report or report template to generate the report. For example: Job Summary.
The Job Summary Scope Selector allows you to specify parameters, report criteria and generate a report as shown in the following example:
2. Click Modify. The Report Scope Selector window launches.
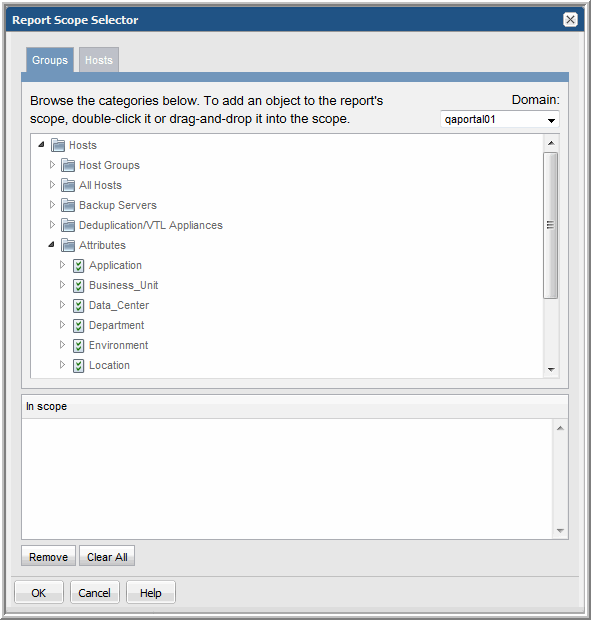
3. On the Groups tab, expand the Hosts folder to view the Attributes folder.
4. Expand the Attributes folder to view the list of attributes that have been created for your environment. Refer to
Managing Attributes and Objects for
details on creating and managing attributes and their values.
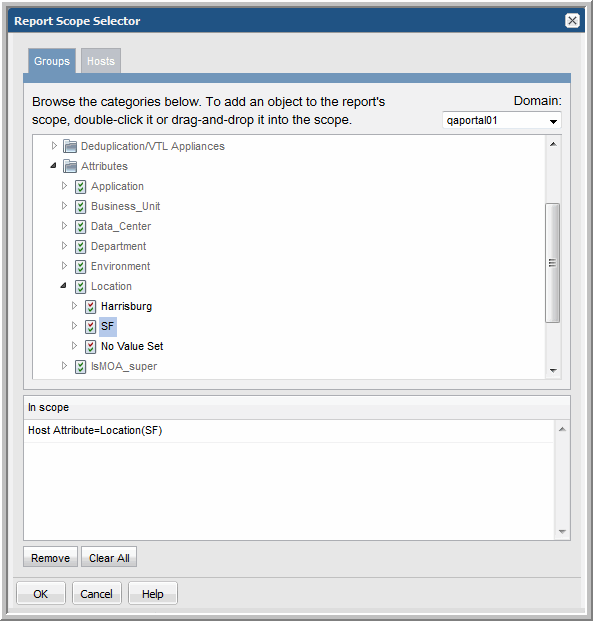
5. Drag the attribute values into the “In scope” pane.
For example, find all hosts where the attribute, Location, is set to SF.
Group Hosts by Attributes
Because many environments have thousands of hosts to manage, it is often necessary to group hosts in a variety of ways to efficiently manage them. Use host attributes to add additional properties to a host to generate reports for discrete sets of hosts. Conversely, you may want to discover what hosts do not have an attribute set. This is also an option. By selecting the attribute
No Value Set enables you to produce a results set without a set attribute value. See also,
Host Groups vs Attributes.
Host Attributes Examples
• Show all hosts owned by Marketing.
• Show the hosts in Europe that belong to Sales.
• Show hosts by location, business unit, and application.
Find Hosts Without an Attribute Value Set
• Show all hosts that have not been tagged with a Location value. This enables you to find hosts that may not be grouped correctly for host management.
• Show all hosts that have not been tagged with a Business Unit.