Load LUN Attributes and Values
Function: The Load LUN Attributes utility provides an efficient method of assigning attributes to a large number of storage array logical units (LUNs).
To load switch attributes and values
4. Create a report template using the SQL Template Designer.
Once attribute values are assigned to application databases, a SQL Template Designer report can query the database to report on the application databases.
Create a CSV File of LUN Objects and Attributes
The loadLunAttributeFile utility assigns attribute values to a list of LUNs. This utility takes as input a comma-separated values (CSV) file.
NOTE: This CSV file becomes the master document of record for LUN Attributes and therefore should be preserved in a working directory for future updates.
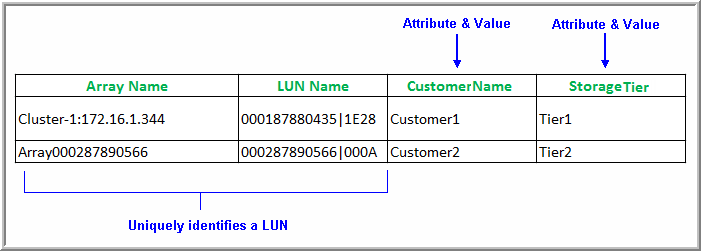
1. Create a spreadsheet table, in the format shown in the following example, and save it as a CSV file in a working directory. This file is specific to loading LUN attributes.
Columns
• The first column lists the Array Name.
• The second column lists the LUN Name.
• Each additional column lists attributes and values that will be applied to the LUN. Multiple attributes can be assigned to a single LUN object.
Rows
• First (Header) Row - Contains the fields that uniquely identify the LUN (array and LUN names), followed by Attribute names. The header row is information only and is not processed as a data row.
• Subsequent rows list the Array name and LUN name, followed by the attribute values that you are assigning to each LUN.
Execute the Load LUN Attribute Utility
Before You Begin
Bulk Load utilities must be run in SQLPLUS as user APTARE. The load_package utility is located in:
/opt/aptare/database/stored_procedures (Linux)
\opt\oracle\database\stored_procedures (Windows)
To assign attributes to application databases
2. Save the table as a comma-separated file (for example, SwitchAttributes.csv).
3. Log in to the Portal server.
4. At the command line:
su - aptare
5. At the command line, launch sqlplus:
sqlplus <pwd>/<pwd>
• Example: sqlplus portal/portal
6. Execute the following at the SQL prompt:
SQL> Execute load_package.loadLunAttributeFile(‘pathname_and_filename’, ‘domain_name’,array_name_column_num, lun_name_column_num ,‘log_path_name’,‘log_file_name’,‘check_valid_value’);
Where:
‘pathname_and_filename’ | Full path + filename (enclosed in single straight quotes) of the CSV file Windows Example: ‘c:\config\SwitchAttributes.csv’ Linux Example: ‘/config/SwitchAttributes.csv’ |
‘domain_name’ | Name (enclosed in single straight quotes) of the domain in which the host groups and hosts reside; Example: ‘DomainEMEA’ |
array_name_column_num | Column number in the csv file where the Array Name is listed; Example: 1 Note that the Array Name and the LUN Name can be either column 1 or 2 of the CSV. This parameter tells the utility in which column the Array Name will be found. |
lun_name_column_num | Column number in the csv file where the LUN Name is listed; Example: 2 |
‘log_path_name’ | Full path (enclosed in single straight quotes) where the log file will be created/updated; verify that you have write access to this directory. Optional: If a log path and filename are not specified, log records are written to scon.log and scon.err. To omit this parameter, enter: ‘’ Example: ‘c:\config’ |
‘log_file_name’ | Log file name enclosed in single straight quotes. Optional: If a log path and filename are not specified, entries are written to scon.log and scon.err. To omit this parameter, enter: ‘’ Example: ‘SwitchAttributes.log’ |
‘check_valid_value’ | ‘Y’ or ‘N’ enclosed in single straight quotes. Y - Checks if the attribute value exists. If the utility determines that the attribute value is not valid, it skips this row and does not assign the attribute value to the switch object. N - Updates without checking that the attribute value exists. This option is seldom chosen, but it is available for certain customer environments where attributes may have been created without values (with scripts that bypass the user interface). |
Example:
SQL> Execute load_package.loadLunAttributeFile(‘/config/LUNAttributes.csv’, ‘DomainEMEA’, 1, 2,‘/config/logs’, ‘LUNAttributes.log’, ‘Y’);
7. Check the log file for status and errors.
8. Restart the Portal services so that the newly added attributes become available in the Dynamic Template Designer.
Verify the LUN Attributes Load
To verify that the attribute load was successful:
1. In the Portal, navigate to Tools > Templates > SQL Template Designer.
2. To verify Switch attributes, use the following query in the SQL Template Designer:
select * from aps_v_logical_unit_attribute