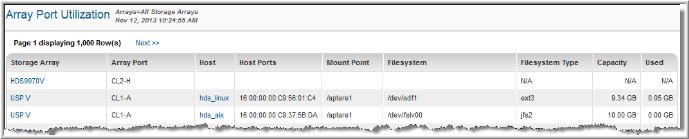

Storage Array | The array links to the Array Capacity and Utilization. You can select multiple storage arrays or a single array when you generate this report. |
Array Port | The array’s port number. |
Host | Name of the host that owns the HBA (host bus adaptor) port. Links to the Host Utilization Detail. |
Host Ports | List of the host ports. Comma-separated string of the WWN of all the HBA ports associated with the array port. |
Mount Point | The mount point of the filesystem that’s utilizing the port. |
Filesystem | Name of the filesystem. |
Filesystem Type | When you know the filesystem type, you can determine the host’s storage requirements and limitations. Examples of filesystem values: NTFS - Windows NT Filesystem ext2, ext3 - Extended Filesystems 2 and 3 ufs - Linux Filesystem vxfs - Veritas Filesystem FAT - File Allocation Table hfs - Hierarchical Filesystem (Apple) ctfs - Cooperative Temporary Filesystem devfs - Device Filesystem hsfs - High Sierra Filesystem jfs - Journaled Filesystem jfs2 - Journaled Filesystem 2 nfs - Network Filesystem objfs - Filesystem Object sfs - Secure Filesystem gpfs - General Parallel Filesystem (IBM) proc - a virtual filesystem procfs - Process Filesystem tmpfs - a virtual memory filesystem smbfs - Server Message Block Filesystem Null - empty NA - not applicable |
Capacity | Capacity of the filesystem. |
Used | The amount of the storage array being used by the filesystem. |